As usual, I'll be delighted if my visitors who use Mac take the time to test the small tool and share their opinion.


{ Screenshots by Floris van Eck. }
Other Google software for Mac:
Picasa Web Uploader, Video Player, Google Earth, Sketchup


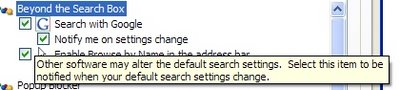
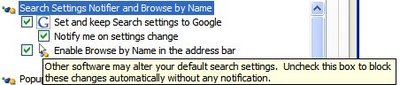

 Google launched many features that deal with saving personal stuff, but the big picture in which all of them will be integrated is yet to be revealed.
Google launched many features that deal with saving personal stuff, but the big picture in which all of them will be integrated is yet to be revealed.
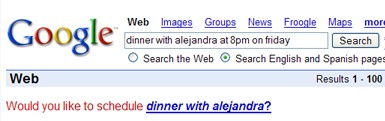
 Writely Blog is proud to announce that Writely access is now free for everyone. Just sign up for an account.
Writely Blog is proud to announce that Writely access is now free for everyone. Just sign up for an account.

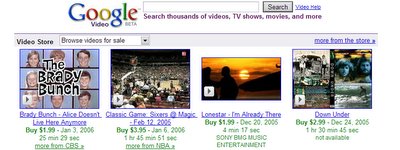








 Well, the post about Gmail avatars used for face recognition has a nice follow up from Google. They've acquired Neven Vision, a company specialized in image recognition.
Well, the post about Gmail avatars used for face recognition has a nice follow up from Google. They've acquired Neven Vision, a company specialized in image recognition.Google Search
<!--googleoff: index-->
Appliance
<!--googleon: index-->
is great.
 New York Times reports that Google will start allowing local businesses to add coupons in Google Maps for free. They hope to attract many small businesses interested in promoting their products to a targeted audience and a lot of freebie hunters, that will visit Google Maps more.
New York Times reports that Google will start allowing local businesses to add coupons in Google Maps for free. They hope to attract many small businesses interested in promoting their products to a targeted audience and a lot of freebie hunters, that will visit Google Maps more.







Like most Web sites, our servers automatically record the page requests made when users visit our sites. These "server logs" typically include your web request, Internet Protocol address, browser type, browser language, the date and time of your request and one or more cookies that may uniquely identify your browser.
Here is an example of a typical log entry where the search is for "cars", followed by a breakdown of its parts:
123.45.67.89 - 25/Mar/2003 10:15:32 - http://www.google.com/search?q=cars - Firefox 1.0.7; Windows NT 5.1 - 740674ce2123e969
* 123.45.67.89 is the Internet Protocol address assigned to the user by the user's ISP; depending on the user's service, a different address may be assigned to the user by their service provider each time they connect to the Internet;
* 25/Mar/2003 10:15:32 is the date and time of the query;
* http://www.google.com/search?q=cars is the requested URL, including the search query;
* Firefox 1.0.7; Windows NT 5.1 is the browser and operating system being used; and
* 740674ce2123a969 is the unique cookie ID assigned to this particular computer the first time it visited Google. (Cookies can be deleted by users. If the user has deleted the cookie from the computer since the last time s/he visited Google, then it will be the unique cookie ID assigned to the user the next time s/he visits Google from that particular computer).



Windows Live Writer is a new tool from Microsoft that allows you to publish to your blog using a desktop client. While the software is integrated with Windows Live Spaces, you can also use it with Blogger, LiveJournal, TypePad, WordPress.
What's nice about Windows Live Writer is that it reads your blog's template and it lets you preview your content while creating it. It's like seeing your blog post growing.
The rich-text editor is not impressing, as it contains the usual elements and doesn't produce clean code (you'll notice many unneeded tags). When you insert pictures, you've got more options: you can resize the picture, add a nice shadow, adjust brightness and even use some simple effects like sepia. Unfortunately, Blogger doesn't allow you to publish images for the hosted blogs.
Windows Live Writer also lets you insert maps using Windows Live Local and the maps can be customized to show the aerial view or bird's eye detail.
When you select the preview mode, you'll see how your blog would look if you published the post, so it takes the idea of preview one step further.
Windows Live Writer is available to download here [4.74 MB, Windows] and it's still beta. The simple interface and the innovative additions make this tool a good replacement for the standard blogging interfaces and it's a good alternative to Performancing for Firefox, Qumana, but it's still far from a commercial application like ecto.


